-

The Geological Survey of Canada initiates exploration of the oil sands of the Athabasca region on the part of the federal government.
Tar Sands, Athabasca River, Alberta, n.d.
Source: Geological Survey of Canada/Library and Archives Canada, PA-038166
-

Drilling in search of a basement reservoir of oil is the initial focus of development in Alberta’s oil sands.
Drilling plant at Victoria, Alberta, 1898
Source: Glenbow Archives, NA-302-11
-

Alfred von Hammerstein is the first independent entrepreneur to attempt to capitalize on the petroleum riches of the oil sands.
Alfred von Hammerstein on horseback, ca. 1900
Source: Glenbow Archives, PA-3920-1
-

The federal government renews its investigation of the oil sands by sending Sidney Ells to Athabasca to conduct field and survey work.
Sidney Ells at Clearwater River tar sands plant, August 1931
Source: Canada. Dept. of Mines and Technical Surveys/Library and Archives Canada, PA-014454
-

Throughout the 1920s, efforts to commercially develop the oil sands focused upon its possible use as a paving surface for roads and sidewalks.
View of demonstration experimental pavement laid in Edmonton, Alberta, 1915
Source: Provincial Archives of Alberta, A3399
-

The Scientific and Industrial Research Council of Alberta is founded.
Henry Marshall Tory, the first president of the University of Alberta, was instrumental in founding the Scientific and Industrial Research Council of Alberta, n.d.
Source: University of Alberta Archives, 69-152-003
-

Karl Clark builds his first model hot-water separation plant.
Karl Clark and Sidney Blair built a model oil sands separation plant in the basement of the University of Alberta power plant.
Source: University of Alberta Archives, 69-97-457
-

Jacob Absher attempts in situ extraction of oil from oil sands.
Absher’s set-up on Saline Creek, near Fort McMurray, 1929
Source: University of Alberta Archives, 77-128-27
-

Robert Fitzsimmons founds the International Bitumen Company Ltd.
Prospectus for the International Bitumen Company Ltd., n.d.
Source: Provincial Archives of Alberta, PR1971.0356.544a,b.ProspectusOf.IBC.1
-

Federal and provincial governments cooperate to develop Clearwater River oil sands separation plant.
Karl Clark’s third model plant is relocated to the Clearwater River. Sidney Ells is placed in charge of mining operations.
Source: University of Alberta Archives, 77-128-13
-

Max Ball, J.M. McClave and B.O. Jones of Denver, Colorado, organize Abasand Oils Ltd.
Max Ball, ca. 1940
Source: University of Alberta Archives, 89-120-008
-
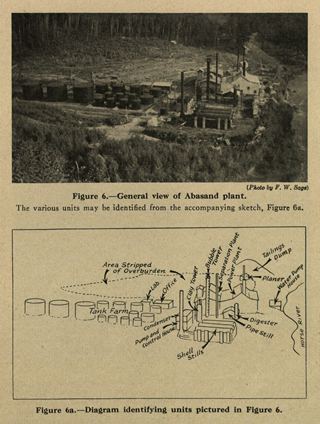
Construction of Abasand Oils Ltd. oil sands separation plant on Horse River is completed.
Abasand Oils Ltd. plant, ca. 1941
Source: Provincial Archives of Alberta, PR1985.0333.DevelopmentofAthabaska.O.S.DeskCopy.021 - detail
-

Abasand Oils Ltd. oil sands separation plant burns down.
Little was left of the Abasand plant after the fire.
Source: University of Alberta, 84-25-132
-

Alberta Government Oil Sands Project Plant at Bitumount succeeds in separating crude oil from oil sands.
The completed Alberta Government Oil Sands Project plant, ca. 1950
Source: University of Alberta, 91-137-070 - detail
-

Alberta government issues report on oil sands potential.
Cover of Sidney Blair’s Report on the Alberta Bituminous Sands commissioned by the Government of Alberta, 1950
Source: Provincial Archives of Alberta, PR1971.0345.box24.503
-

Athabasca Oil Sands Conference establishes an Alberta oil sands policy and stimulates commercial interest in the resource.
Sidney Kidder, Sidney Blair, George Hume, and Elmer Adkins (l to r) at the Edmonton portion of the Athabasca Oil Sands Conference at the University of Alberta, 1951
Source: Provincial Archives of Alberta, PA3152
-

Great Canadian Oil Sands Ltd. incorporates.
Montreal-businessman Lloyd Champion incorporates Great Canadian Oil Sands Ltd. (GCOS) in 1953. Champion, shown here ca. 1960s, later sells most of his shares in the company before the GCOS plant opens under Sun Oil Company’s financing and leadership.
Source: University of Alberta Archives, #83-160
-
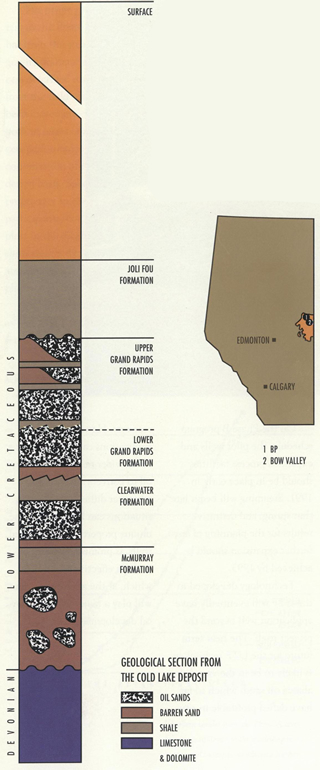
Early in situ pilot tests begin on the Peace River and Cold Lake area oil sands deposits; underground experiments along the Cold Lake deposit lead to the development of the Cyclical Steam Stimulation (CCS) bitumen recovery method.
A cross-section of the Cold Lake area deposit shows the depth of the oil sands layer that makes the bitumen in this deposit recoverable only through in situ extraction methods.
Source: Courtesy of Alberta Innovates
-

Great Canadian Oil Sands Ltd. begins production.
Great Canadian Oil Sands Ltd. plant during its first week of operation, north of Fort McMurray, Alberta, 1967
Source: Courtesy of Suncor
-

Global oil crisis heightens conflict between Alberta and Ottawa.
Canada’s Prime Minister Pierre Elliott Trudeau and Alberta Premier Peter Lougheed, November 1, 1977; Trudeau and Lougheed clash over oil sands ownership, export taxation and natural resource revenue sharing arrangements.
Source: Provincial Archives of Alberta, J3672.2
-
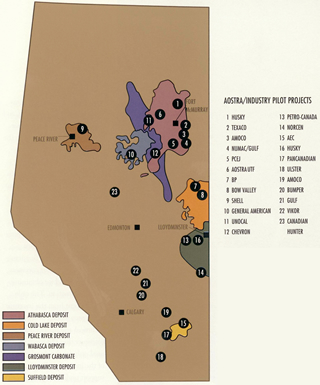
Alberta Oil Sands Technology and Research Authority (AOSTRA) forms as a Crown corporation.
A map of Alberta shows AOSTRA/industry in situ pilot projects that emerge in the 1970s and 1980s
Source: Courtesy of Alberta Innovates
-

Historic Winnipeg meeting between government and industry leads to agreement on Syncrude consortium mega-project.
A news story published in the Winnipeg Tribune on February 4, 1975, reports the anticipated agreement that enables completion of the Syncrude consortium’s mega-project.
Source: The Winnipeg Tribune
-

Syncrude opens oil sands mining and bitumen upgrading mega-project in northeastern Alberta.
Syncrude operations near Mildred Lake north of Fort McMurray, late 1970s
Source: Courtesy of Syncrude Canada Ltd.
-
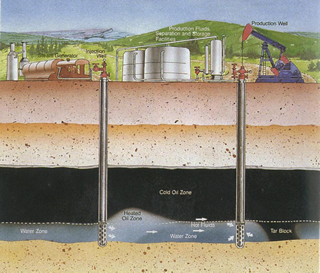
Partnership between industry and the Alberta Oil Sands Technology and Research Authority (AOSTRA) leads to commercialization of in situ recovery methods.
AOSTRA-sponsored technology develops through the late 1970s and early 1980s; the Cyclic Steam Stimulation bitumen recovery process injects steam through one well below the base of the oil sands, resulting in a heat zone that mobilizes the bitumen so that it can be pumped to the surface through a second production well.
Source: Courtesy of Alberta Innovates
-
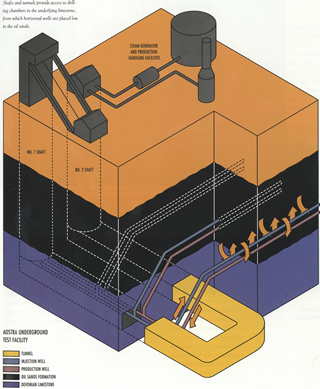
Alberta Oil Sands Technology and Research Authority (AOSTRA) formally opens its Underground Test Facility to field test in situ oil sands mining theory including the industry-changing Steam-Assisted Gravity Drainage method (SAGD).
A diagram of AOSTRA’s Underground Test Facility operations
Source: Courtesy of Alberta Innovates